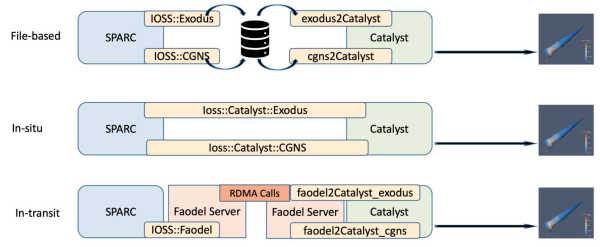
FAODEL 1.2108.1 Released
We received DOE approval to relase version 1.2108.1 ("Fluid") of FAODEL on Github.

We received DOE approval to relase version 1.2108.1 ("Fluid") of FAODEL on Github.

Our ASCR project published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) report on arXiv.

High-performance computing (HPC) researchers have long envisioned scenarios where application workflows could be improved through the use of programmable processing elements embedded in the network fabric. Recently, vendors have introduced programmable Smart Network Interface Cards (SmartNICs) that enable computations to be offloaded to the edge of the network. There is great interest in both the HPC and high-performance data analytics communities in understanding the roles these devices may play in the data paths of upcoming systems.
This paper focuses on characterizing both the networking and computing aspects of NVIDIA's new BlueField-2 SmartNIC when used in an Ethernet environment. For the networking evaluation we conducted multiple transfer experiments between processors located at the host, the SmartNIC, and a remote host. These tests illuminate how much processing headroom is available on the SmartNIC during transfers. For the computing evaluation we used the stress-ng benchmark to compare the BlueField-2 to other servers and place realistic bounds on the types of offload operations that are appropriate for the hardware.
Our findings from this work indicate that while the BlueField-2 provides a flexible means of processing data at the network's edge, great care must be taken to not overwhelm the hardware. While the host can easily saturate the network link, the SmartNIC's embedded processors may not have enough computing resources to sustain more than half the expected bandwidth when using kernel-space packet processing. From a computational perspective, encryption operations, memory operations under contention, and on-card IPC operations on the SmartNIC perform significantly better than the general-purpose servers used for comparisons in our experiments. Therefore, applications that mainly focus on these operations may be good candidates for offloading to the SmartNIC.
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) technical report.

The performance of NVIDIA's latest A100 graphics processing unit (GPU) is benchmarked for computing and data analytic workloads relevant to Sandia's missions. The A100 is compared to previous generations of GPUs, including the V100 and K80, as well as multi-core CPUs from two generations of AMD's EPYC processors, Zen and Zen 2. Computing workloads such as sparse matrix operations (e.g. HPCG benchmark) and numerical solver-heavy applications based on Trilinos and Kokkos see a moderate 1.5x to 2x speedups compared to the V100, consistent with the increased core count and memory bandwidth of the A100. Training and inference on machine learning (ML) models such as ResNet-50 for image classification and BERT-Large for natural language processing show the same 2x speedup over the V100.
However, these ML workloads also benefit from increased tensor core capabilities in the V100 and A100 GPUs, yielding a 3.5x speedup using a mixed (single + half) precision strategy for floating point operations. While the performance gap between GPUs and CPUs remains moderate (3x to 8x) for high-performance computing applications, these new hardware features of recent GPU generations give 50x to 100x speedups in out-of-the-box ML workloads compared to CPUs. With additional A100 features still undergoing testing (INT8, structural sparsity, multi-instance GPUs) with clear applications for ML workloads, the A100 GPU seems an extremely promising hardware accelerator for artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics research at Sandia.
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper.
Priority-based Flow Control (PFC), RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) and Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) are three enhancements to Ethernet networks which allow increased performance and may make Ethernet attractive for systems supporting a diverse scientific workload. We constructed a 96-node testbed cluster with a 100 Gb/s Ethernet network configured as a tapered fat tree. Tests representing important network operating conditions were completed and we provide an analysis of these performance results. RoCE running over a PFC-enabled network was found to significantly increase performance for both bandwidth-sensitive and latency-sensitive applications when compared to TCP. Additionally, a case study of interfering applications showed that ETS can prevent starvation of network traffic for latency-sensitive applications running on congested networks. We did not encounter any notable performance limitations for our Ethernet testbed, but we found that practical disadvantages still tip the balance towards traditional HPC networks unless a system design is driven by additional external requirements.
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) technical report.