We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper.

Abstract
Scientific and technical publications can provide relevant information regarding the technical capabilities of a state, the location of nuclear materials and related research activities within that state, and international partnerships and collaborations. Nuclear proliferation analysts monitor scientific and technical publications using complex word searches defined by fuel cycle experts as part of their collection and analysis of all potentially relevant information. These search strings have been refined over time by fuel cycle experts and other analysts but represent a top-down approach that is inherently defined by the requirement of term presence. In contrast, we are developing a bottom-up approach in which we develop topic models from a small number of expert refereed source documents to search similar topic space, with the hope that we can use this method to identify publications that are relevant to the proliferation detection problems space without necessarily conforming to the expert-derived rule base. We are comparing our results of various topic modeling and clustering techniques to a traditional analyst search strings to determine how well our methods work to find seed documents. We also present how our methods provide added benefit over traditional search by organizing the retrieved documents into topic-oriented clusters. Finally, we present distributions of author institutions to facilitate a broader perspective of the content of interest for analysts.
Publications
- INMM Paper Jonathan Bisila, Daniel M. Dunlavy, Zoe N. Gastelum, and Craig D. Ulmer, "Topic Modeling with Natural Language Processing for Identification of Nuclear Proliferation-Relevant Scientific and Technical Publications", in Proceedings of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM) 61st Annual Meeting, July 12, 2020.
Presentations
- INMM Slides Presentation that Jon gave virtually at INMM.
2020-05-28 Thu
faodel net pub
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper.
Abstract
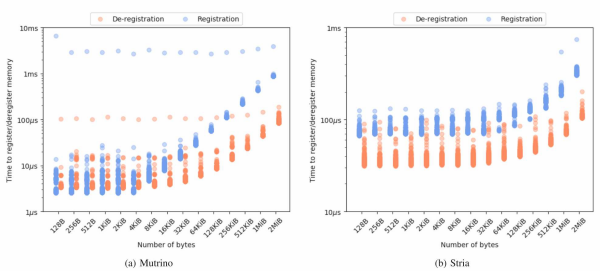
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) is an increasingly important technology in high-performance computing (HPC). RDMA provides low-latency, high-bandwidth data transfer between compute nodes. Additionally, it does not require explicit synchronization with the destination processor. Eliminating unnecessary synchronization can significantly improve the communication performance of large-scale scientific codes. A long-standing challenge presented by RDMA communication is mitigating the cost of registering memory with the network interface controller (NIC). Reusing memory once it is registered has been shown to significantly reduce the cost of RDMA communication. However, existing approaches for reusing memory rely on implicit memory semantics. In this paper, we introduce an approach that makes memory reuse semantics explicit by exposing a separate allocator for registered memory. The data and analysis in this paper yield the following contributions: (i) managing registered memory explicitly enables efficient reuse of registered memory; (ii) registering large memory regions to amortize the registration cost over multiple user requests can significantly reduce cost of acquiring new registered memory; and (iii) reducing the cost of acquiring registered memory can significantly improve the performance of RDMA communication. Reusing registered memory is key to high-performance RDMA communication. By making reuse semantics explicit, our approach has the potential to improve RDMA performance by making it significantly easier for programmers to efficiently reuse registered memory.
Publication
- IPDPSW Paper Scott Levy, Patrick Widener, Craig Ulmer, and Todd Kordenbrock, "The Case for Explicit Reuse Semantics for RDMA Communication", 2020 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW) pp 879-888. DOI:10.1109/IPDPSW50202.2020.00148
2019-12-01 Sun
hpc io faodel pub
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper.
Abstract
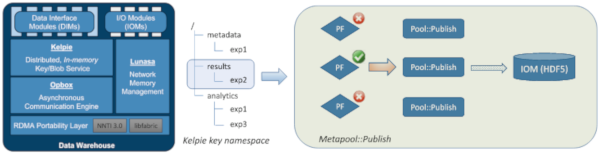
Composition of computational science applications into both ad hoc pipelines for analysis of collected or generated data and into well-defined and repeatable workflows is becoming increasingly popular. Meanwhile, dedicated high performance computing storage environments are rapidly becoming more diverse, with both significant amounts of non-volatile memory storage and mature parallel file systems available. At the same time, computational science codes are being coupled to data analysis tools which are not filesystem-oriented. In this paper, we describe how the FAODEL data management service can expose different available data storage options and mediate among them in both application- and FAODEL-directed ways. These capabilities allow applications to exploit their knowledge of the different types of data they may exchange during a workflow execution, and also provide FAODEL with mechanisms to proactively tune data storage behavior when appropriate. We describe the implementation of these capabilities in FAODEL and how they are used by applications, and present preliminary performance results demonstrating the potential benefits of our approach.
Publications
- ISC HP Paper Patrick Widener, Craig Ulmer, Scott Levy, Todd Kordenbrock, and Gary Templet, "Mediating Data Center Storage Diversity in HPC Applications with FAODEL", ISC High Performance 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11887.
Presentations
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) technical report.

Abstract
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) has the potential to provide performance that rivals traditional high performance fabrics. If this potential proves out, significant impacts on system procurement decisions could follow. This work provides a series of small scale performance results which are used to compare and contrast the performance of RoCE-enabled Ethernet with TCP-based Ethernet and an HPC network. Additionally, a discussion of the maturity of RoCE firmware/software stacks and documentation is provided along with useful approaches for probing performance. A detailed description of two experimental setups known to have good RoCE performance is given, including step-by-step configuration and the exact hardware and software revisions employed. At small scales, RoCE is found to have significant performance advantages over "out-of-the-box" TCP protocols and is competitive with state-of-the-art high performance networks. Further examination of RoCE using a wider array of benchmarks and at greater scale is warranted.
Publication
- SAND Report Joseph Kenny and Craig Ulmer "RoCE Promising Technology for Ethernet as a High Performance Networking Fabric". SAND2019-13444, October 2019.
2019-09-02 Mon
net interns pub
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) technical report.

Publication
- SAND Report Haoda Wang, Gavin Baker, Joseph Kenny, and Craig Ulmer "An Initial Investigation of the Design Challenges Associated with Reliable 100GigE Packet Capture". SAND2019-10319, September 2019.




