Leveraging KeyValue Stores in HPC
I have an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) talk at Salishan about our recent Key/Value store work in HPC.

Presentations
- Salishan Slides: Presentation given at Salishan. SAND2013-3288C (OSTI 1083830)
I have an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) talk at Salishan about our recent Key/Value store work in HPC.

A team I was on won an NNSA Defense Program Award of Excellence.

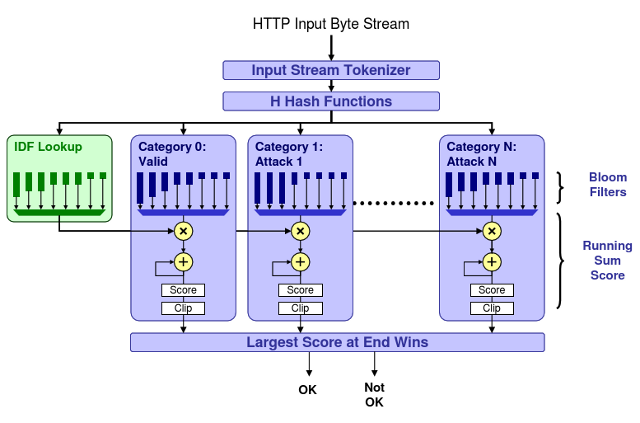
We published unclassified unlimited release (UUR) papers on detecting web attacks in FPGA network filters via Bloom filter arrays.
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper and technical report comparing different storage-focused analytic platforms.

As scientific computing users migrate to petaflop platforms that promise to generate multi-terabyte datasets, there is a growing need in the community to be able to embed sophisticated data analysis algorithms in the storage systems for the computing platforms. Data Warehouse Appliances (DWAs) are an attractive option for this work, due to their ability to process massive datasets efficiently. While DWAs have been proven effective in data mining and informatics applications, there are relatively few examples of how DWAs can be integrated into the scientific computing workflow. In this paper we present our experiences in adapting two mesh analysis algorithms to function on two different DWAs: a SQL-based Netezza database appliance and a Map/Reduce-based Hadoop cluster. The main contribution of this work is insight into the differences between the two platforms' programming environments. In addition, we present performance measurements for entry-level DWAs to help provide a first-order comparison of the hardware.
We published an unclassified unlimited release (UUR) paper.
The field of high performance computing (HPC) currently abounds with excitement about the potential of a broad class of things called accelerators. And, yet, few accelerator based systems are being deployed in general purpose HPC environments. Why is that? This article explores the challenges that accelerators face in the HPC world, with a specific focus on FPGA based systems. We begin with an overview of the characteristics and challenges of typical HPC systems and applications and discuss why FPGAs have the potential to have a significant impact. The bulk of the article is focused on twelve specific areas where FPGA researchers can make contributions to hasten the adoption of FPGAs in HPC environments.